Polyurethane Foam (PUF) panels have gained significant popularity in the construction industry as effective insulation solutions. One crucial parameter that plays a vital role in assessing the insulation performance of these panels is the “K-value.” In this article, we will delve into the concept of the K-value and its significance in the context of PUF panels.
Understanding K-Value:
The K-value, also known as the thermal conductivity or thermal transmission coefficient, represents the material’s ability to conduct heat. It is measured in watts per meter-kelvin (W/m·K) and signifies how well a material can resist the transfer of heat. In the case of PUF panels, a lower K-value indicates better insulation properties, as it implies reduced heat conductivity.
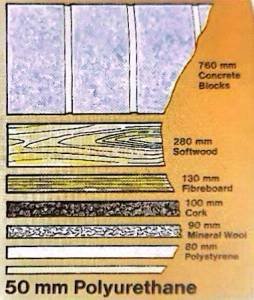
Factors Affecting K-Value in PUF Panels:
Material Composition:
-
- The primary component of PUF panels is polyurethane foam, which consists of polymer chains trapping in targeted inert gas. The arrangement and density of these chains influence the K-value. Generally, panels with higher foam density tend to have lower K-values, indicating better insulation.
-
Cell Structure:
- The cellular structure of the polyurethane foam within the panels is crucial. Closed-cell foams have lower thermal conductivity than open-cell foams, as the closed cells trap specific inert gas and inhibit heat transfer.
-
Thickness:
- The thickness of PUF panels directly affects their insulating capabilities. Thicker panels often have lower K-values because they provide a more substantial barrier to heat transfer.
-
Facing Material:
- PUF panels typically have facing materials on both sides. The type and properties of these facing materials can impact the overall insulation performance. Some facing materials may enhance the panels’ resistance to moisture, which is essential for long-term efficiency.
So far, we are clear that the K-value reveals the material’s thermal conductivity. The lower the value, the more the insulation.
One approach for the design engineer is to refer to the building code for insulation requirements and then determine the PUF Panel thickness accordingly.
-
Energy Efficiency:
- Buildings with high-quality insulation, characterized by low K-values, are more energy-efficient. PUF panels with low K-values contribute to maintaining desired temperatures with minimal energy consumption.
-
Cost Savings:
- Buildings equipped with PUF panels featuring low K-values require less heating or cooling energy, resulting in reduced operational costs over time. This makes them a cost-effective choice for both residential and commercial applications.
-
Environmental Impact:
- Lower K-values translate to reduced energy consumption, contributing to a smaller carbon footprint. Choosing PUF panels with low K-values aligns with sustainable and environmentally friendly construction practices.
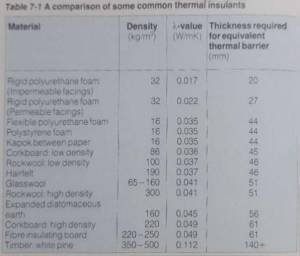
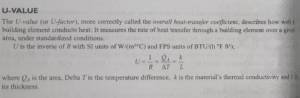
Conclusion:
In the realm of construction and insulation, understanding the K-value of PUF panels is paramount. The proper selection of panels with optimal K-values ensures energy-efficient buildings, cost savings, and a positive environmental impact. As technology advances, manufacturers continue to innovate, providing PUF panels with increasingly lower K-values, further enhancing their effectiveness in creating well-insulated and sustainable structures.


